Configuring the Inbound Gateway requires changes to an organization's own DNS and email service infrastructure, as well as enabling the Gateway inside your Coro workspace.
To route your incoming email traffic via the Inbound Gateway, you need to:
- Obtain all prerequisites.
- Configure your email service to recognize and allow incoming email from Coro's Inbound Gateway. See Setting Coro as an inbound gateway with the original email provider.
- Configure Coro with details of your email domain and SMTP relays so checked email messages can be forwarded to your email service. See Changes required within your Coro workspace.
- Add Coro as the top-level Mail Exchange (MX) record in your organization's DNS settings, ensuring that incoming email is directed to the Inbound Gateway. See Updating your email domain DNS settings.
As this procedure has potential for service disruption, Coro includes test mechanisms to ensure correct configuration and communication between your email service and the Inbound Gateway before you update your DNS settings to begin mail routing. To learn more, see Testing your configuration.
Coro also recommends scheduling these changes at a time of least impact.
Before you begin, make sure you have the following information:
- IP address(es) of Coro’s Inbound Gateway email proxy service. Contact Coro Support for details.
- Mail Exchange (MX) record details for Coro’s Inbound Gateway email proxy service. Contact Coro Support for details.
- The identity of your email service provider
- Your email domain
Coro can be configured with the following email providers:
If you use (or plan to use) Coro's Security Awareness Training module in addition to the Inbound Gateway, refer to Adding Coro's sender IP address as an inbound mail gateway for details of how to configure Gmail for both services.
Sign in to the Google Workspace admin console with your administrator credentials.
Select Apps > Google Workspace > Gmail.
Google displays the Settings for Gmail page:
Locate and select Spam, Phishing and Malware:
From the Spam, phishing, and malware page, select Inbound gateway:
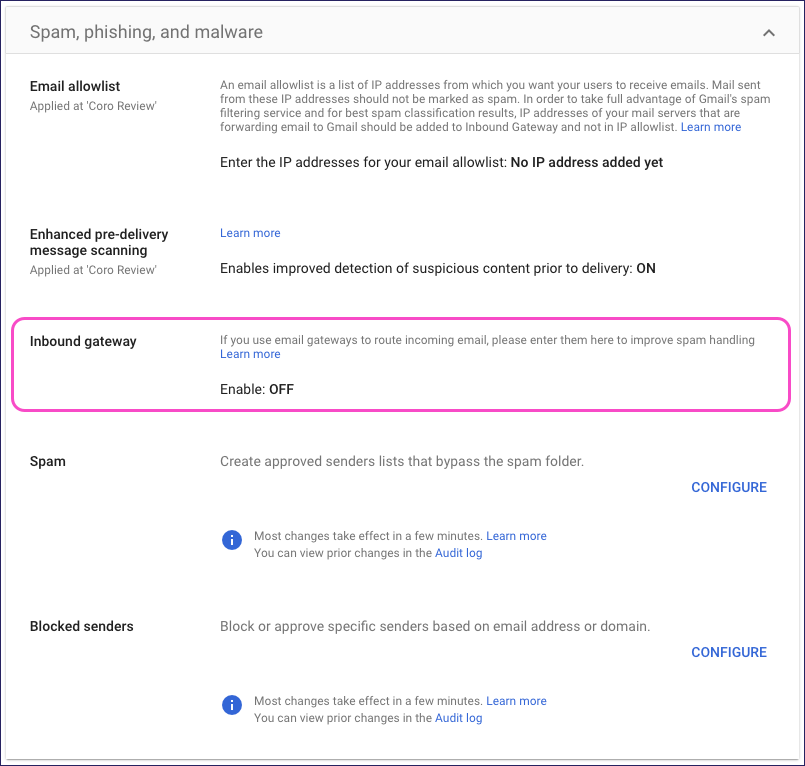
In the Inbound gateway dialog, select Enable, then enter the following settings:
Gateway IPs: Add the Inbound Gateway IP address list.
Google requires you to add each IP address individually. Select ADD and enter a single address from the list, then select Save. Repeat for each IP address.
Automatically detect external IP (recommended): Enable.
Reject all mail not from gateway IPs: Disable.
Require TLS for connections from the email gateways listed above: Enable.
Message is considered spam if the following header regexp matches: Disable.
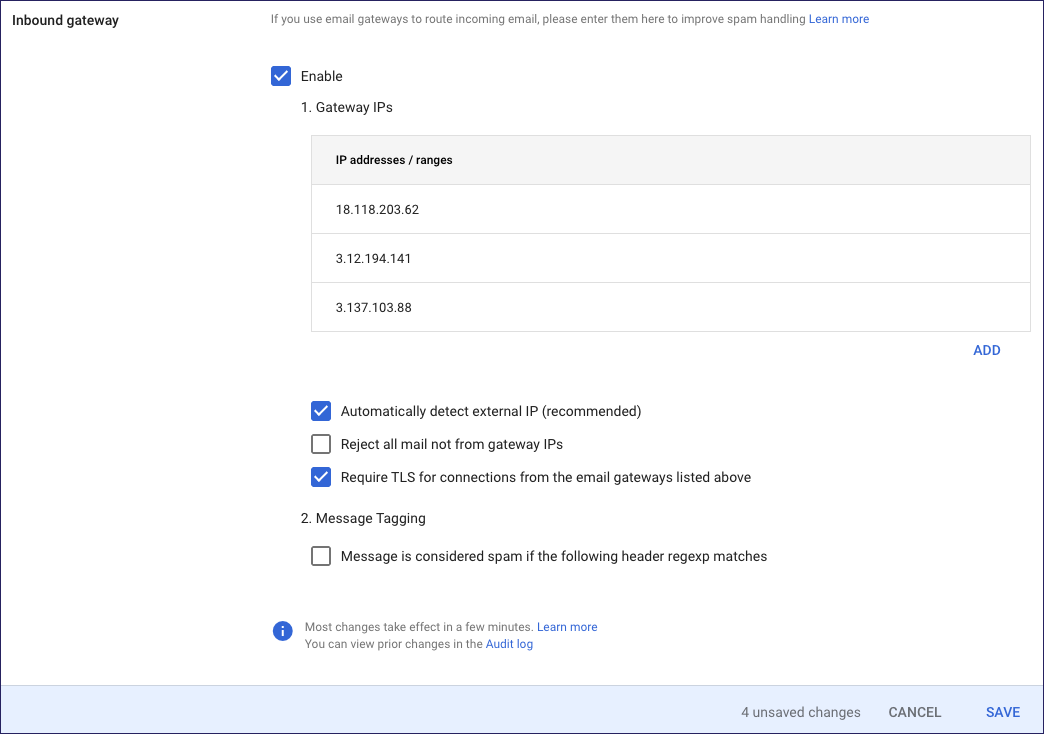
Select SAVE to save your changes.
By specifying Coro Inbound Gateway IP addresses in the Inbound gateway setting, Gmail does not then perform Sender Policy Framework (SPF) or Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) checks on incoming messages.
To configure Microsoft 365 (M365) with Coro, perform the following operations:
- Add Coro's Inbound Gateway IP addresses to your M365 email connection filter allowlist
- Create an inbound email connector based on Coro
- Enable enhanced filtering for the new connector
To add Coro's Inbound Gateway IP addresses to your M365 email allowlist:
Sign into Microsoft Security admin center with your administrator credentials.
Go to Email & Collaboration > Policies & Rules > Threat policies.
Select Anti-spam:
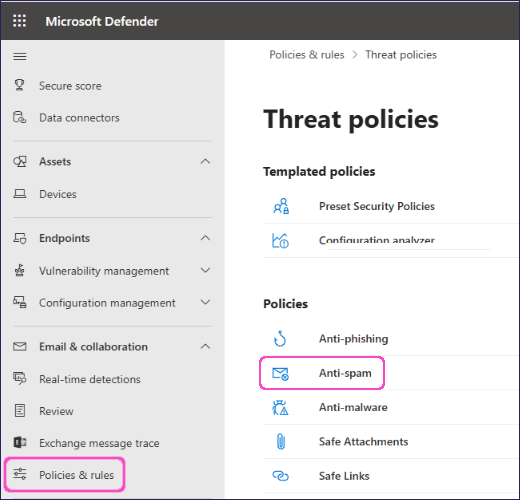
Security admin center displays the Anti-spam policies screen.
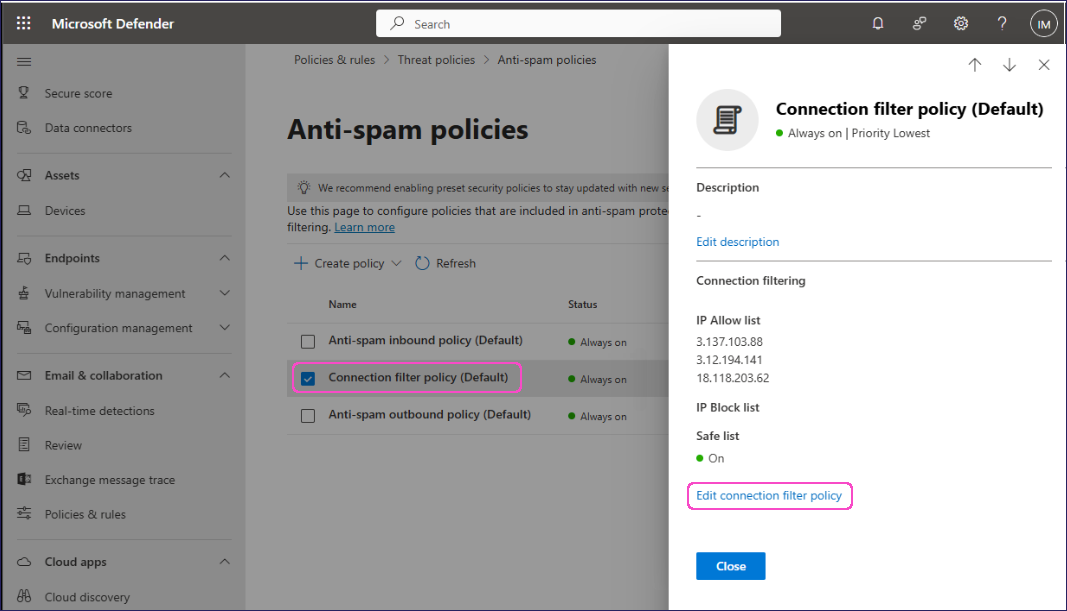
Select Connection filter policy (Default). Then, in the policy dialog, select Edit connection filter policy:
For Always allow messages from the following IP addresses or address range, enter the IP addresses of Coro's Inbound Gateway as provided by Coro Support. Then, enable Turn on safe list:
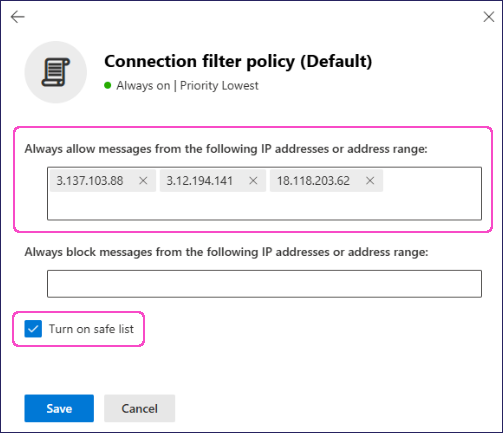
Select Save.
Microsoft recommends disabling SPF Hard fail when an email solution such as Coro's Inbound Gateway is placed in front of it. Return to Email & Collaboration > Policies & Rules > Threat policies > Anti-spam.
Select Anti-spam inbound policy (Default), then locate and select Edit spam threshold and properties:
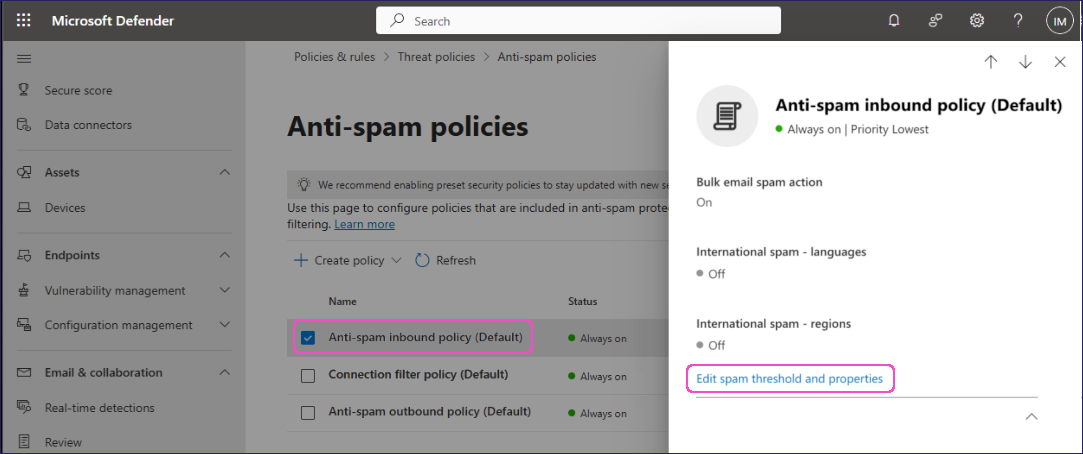
In the Spam threshold and properties dialog, locate and set SPF record: hard fail to Off:
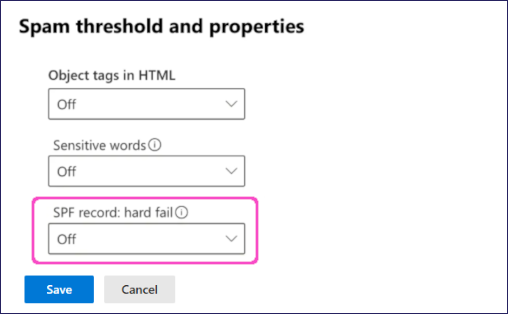
Select Save.
To create an inbound email connector for Coro in Microsoft Exchange admin center:
Sign into Microsoft Exchange admin center with your administrator credentials.
Go to Mail flow > Connectors.
In the Connectors page, select + Add a connector:
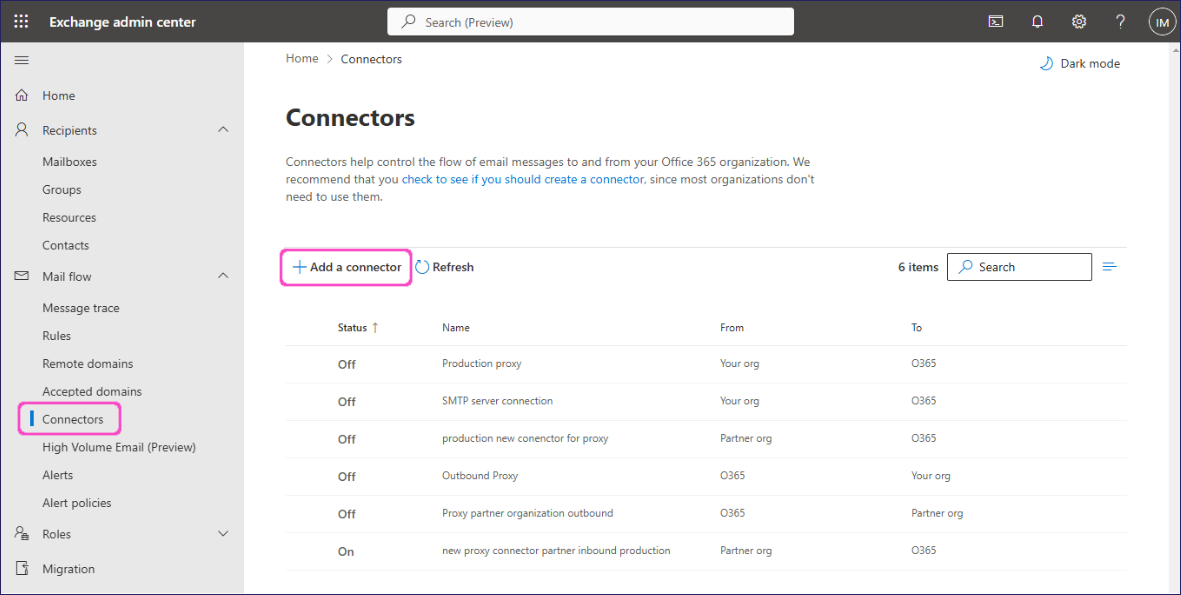
Exchange admin center displays the Add a connector dialog, starting at the New connector step.
For Connection from, select Partner organization.
Select Next to continue.
In the Name step: Add a name describing the incoming mail connection. For example, “Coro email security inbound connection".
Select Next to continue.
In the Authenticating sent email step: select By verifying that the IP address of the sending server matches one of the following IP addresses, which belongs to your partner organization, then enter the IP addresses of Coro's Inbound Gateway as provided by Coro Support:
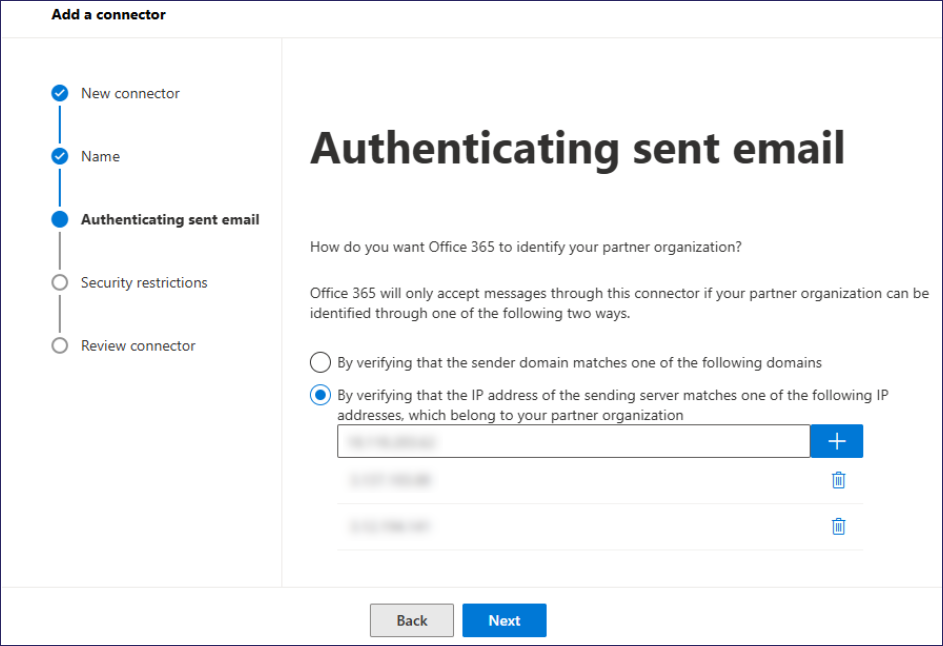
Select Next to continue.
In the Security restrictions step: select Reject email messages if they aren't sent over TLS.
Select Next to continue.
In the Review connector step: Review your settings, then select Create connector.
M365 creates Your new connector based on the settings you provided.
To enable the enhanced filtering configuration of the new Coro connector in the Microsoft Defender admin center:
Sign into Microsoft Security admin center with your administrator credentials.
Go to Email & Collaboration > Policies & Rules > Threat policies.
Select Enhanced filtering:
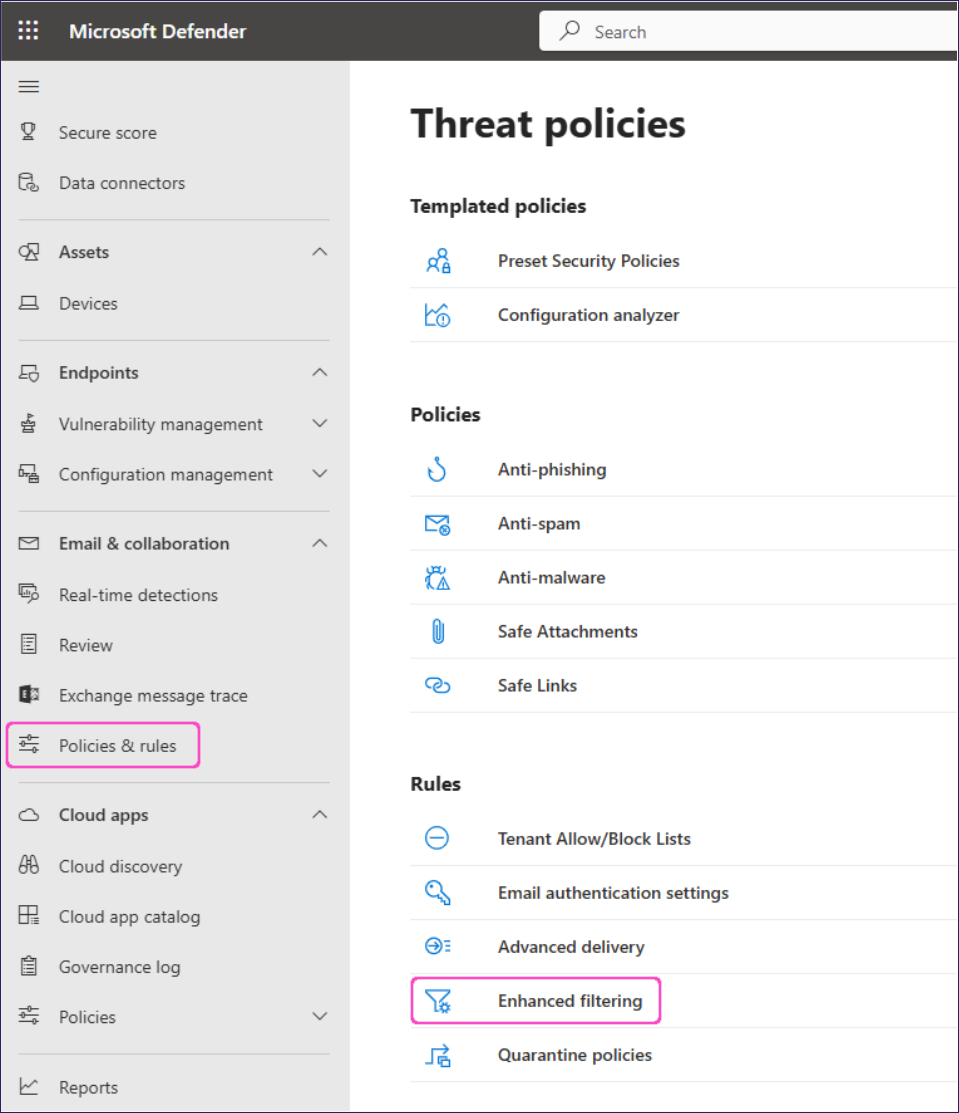
Select the Coro inbound connector you configured in the previous section.
In the detail pane for your connector, select Automatically detect and skip the last IP address and Apply to entire organization:
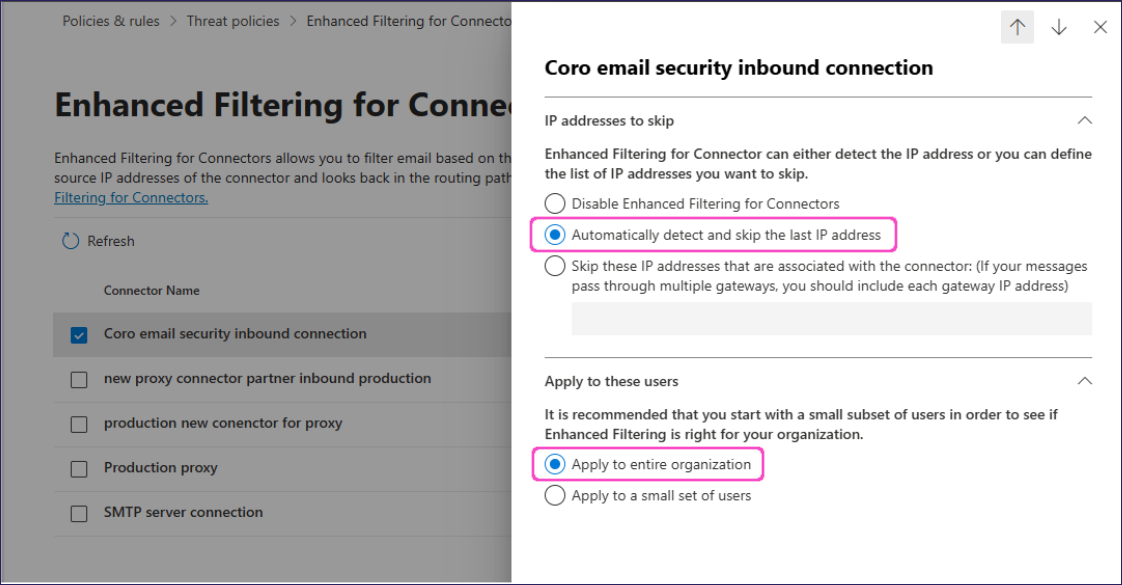
Select Save.
Due to the way Microsoft verifies third party servers configured in your mail flow connectors, you might see Sender Policy Framework (SPF) authentication failures in the headers of your email messages relating to the Coro email proxy. This is to be expected and does not affect processing or delivery of your emails. For more details, contact Coro Support.
Coro can support other third party MTAs that are capable of receiving emails from an inbound email proxy gateway, skipping SPF/DMARC and similar checks. Coro recommends contacting the support team for your MTA to clarify what settings should be applied. For further assistance, contact Coro Support.
After configuring your DNS and email services, enable the Inbound Gateway in your Coro workspace.
Before you begin this procedure, make sure you have the following information:
- Your email domain name
- The list of Mail Exchange (MX) records associated with the domain
To enable the Coro Inbound Gateway:
From the sidebar, select Control Panel. Next, select Gateway Settings:
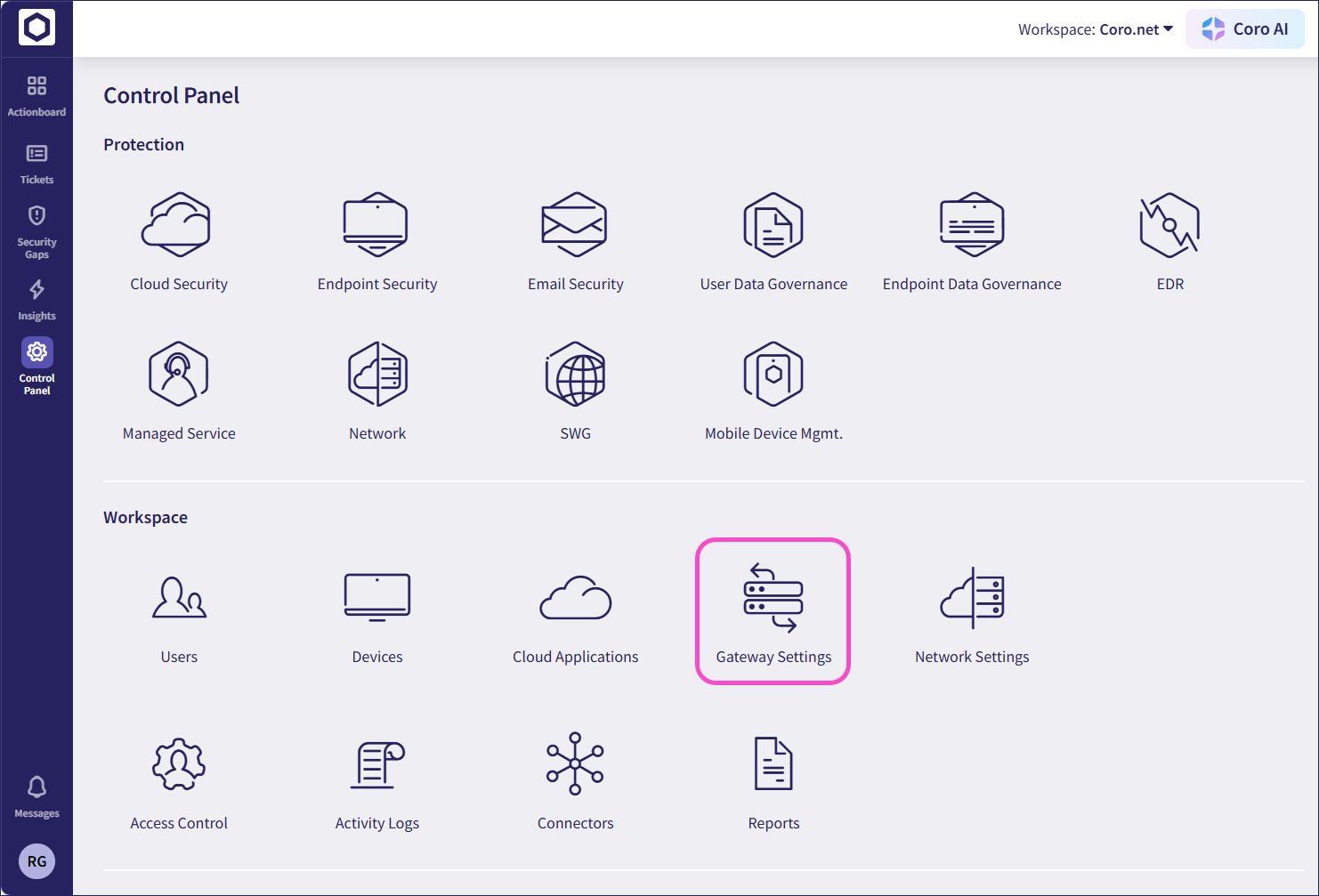
Select Inbound Gateway:
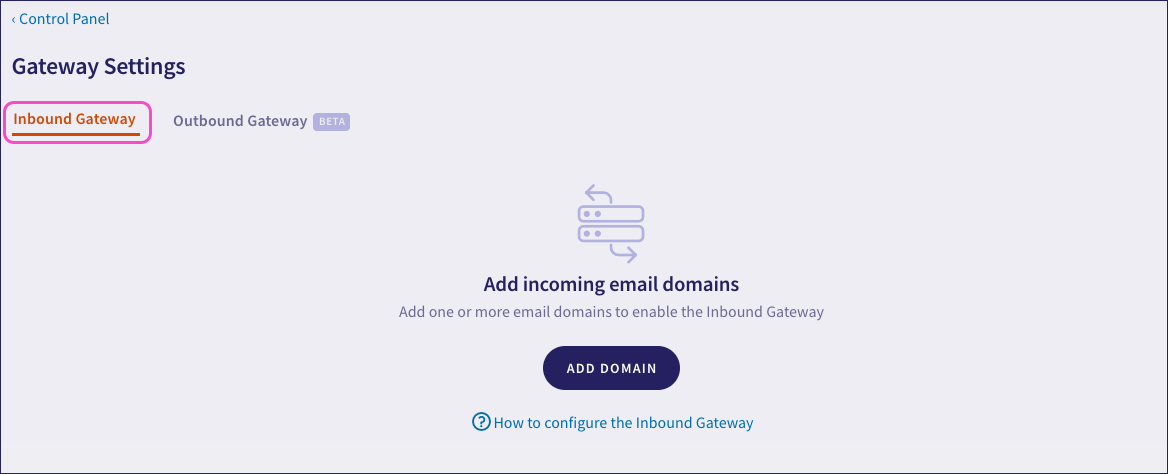
Select ADD DOMAIN:

Coro displays the Add an email domain dialog:
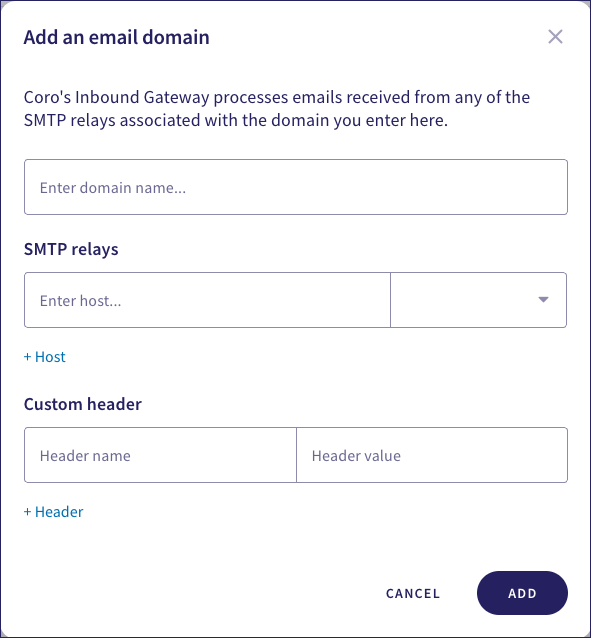
Enter the following settings:
- Enter domain name: Specify the domain for your email service.
- SMTP relays: Enter the list of MX domains to which emails are forwarded by Coro, typically as listed in your current DNS settings (see Updating your email domain DNS settings). For each entry, select port 25 (or the port number relevant to your settings) from the dropdown list.
- Custom header: (Optional) Enter a header name and value for one or more additional custom headers you want to attach to emails handled by the Inbound Gateway. Use this feature where the Inbound Gateway is acting as a relay and you want to identify incoming emails for additional processing or archiving within your organization.
Select ADD to save your settings and close the dialog.
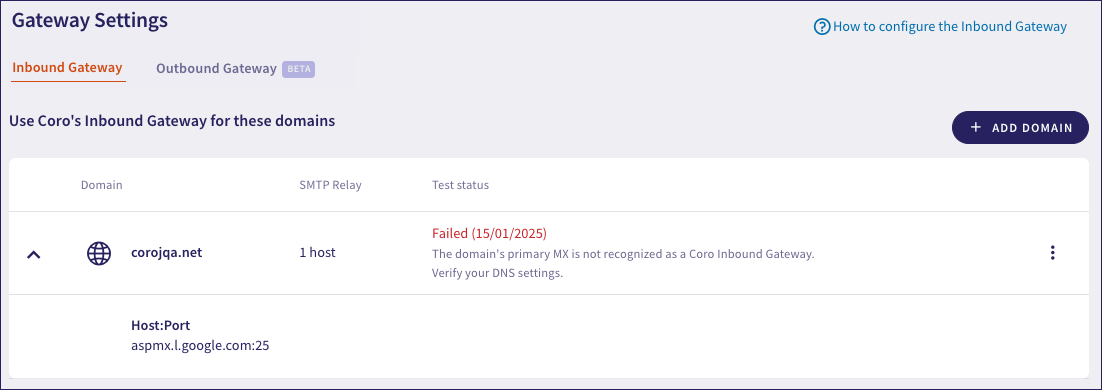
On the Inbound Gateway tab, your new email domain is shown in the table with a status of Not tested:
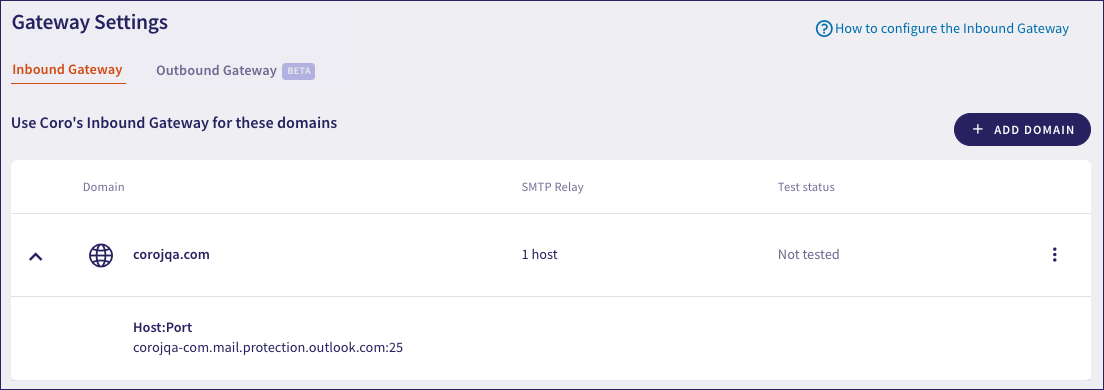
Proceed to test your configuration.
Coro updates the domain's Test Status field to reflect the result of the test.
Configuration of the Inbound Gateway is now complete.
You can test your Inbound Gateway configuration directly from the Coro console:
- Test configuration: A configuration test to confirm that your email provider and Coro workspace are correctly configured to send and receive emails. Use this test to verify your settings before adding Coro to your DNS service.
- Test connection: A full end-to-end test to confirm that your services can communicate and your DNS settings are correctly configured to route email as expected.
To ensure your Inbound Gateway is correctly configured and ready to process incoming emails without disrupting your existing service, Coro recommends first configuring your email provider and Coro workspace before changing your DNS settings. Through this approach, you can perform a configuration test to confirm that the Inbound Gateway can transmit emails successfully to your original provider. After this, you can configure your DNS settings to redirect incoming email to the Inbound Gateway and perform a connection test to verify full end-to-end service.
To test your Inbound Gateway configuration:
On the Inbound Gateway tab, select the three-dot menu adjacent to your domain entry, then select your required test:
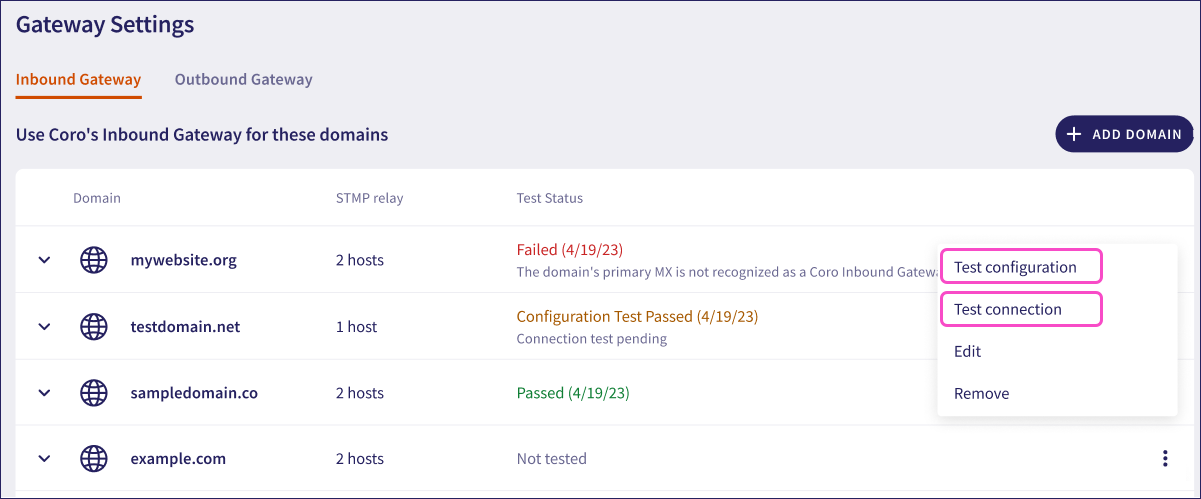
For Test configuration:
Coro displays the Test gateway configuration dialog:
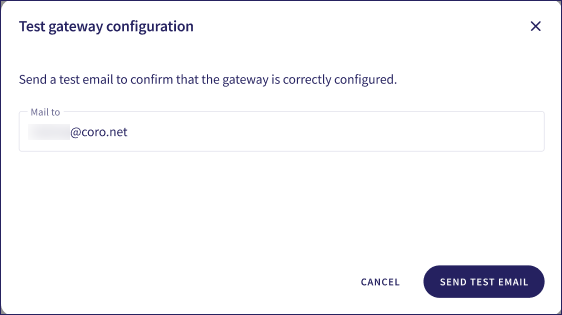
Specify a valid email address at your domain in Mail to, then select SEND TEST EMAIL. If your configuration is correct, Coro sends a test email to this address.
For Test Connection:
Coro displays the Test gateway connection dialog:
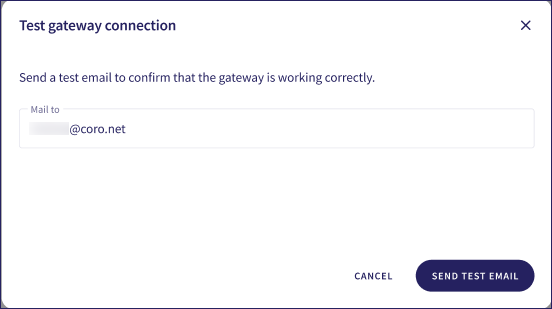
Specify a valid email address at your domain in Mail to, then select SEND TEST EMAIL. If your configuration and DNS settings are correct, Coro sends a test email to simulate incoming email to your domain.
Locate and open the received test email, then select the enclosed link to confirm delivery. If the email is not immediately present in your inbox, check your spam folder.
The domain's Test Status field is updated to reflect the result of the test. Refer to the displayed message for details and reasons for any failure.
A common cause of failure can be incorrect SMTP relay settings. For further advice and assistance, contact Coro Support.
Updating your live DNS settings can cause inbound emails to be immediately routed to Coro's Inbound Gateway. To avoid service interruption or potential data loss, Coro recommends first making sure you have configured your email service for the Inbound Gateway, configured your Coro workspace with details of your email domain, and tested the configuration to ensure correct operation.
To enable Coro to analyze incoming emails, add Coro’s Inbound Gateway server address as a highest-priority Mail Exchange (MX) record in your DNS settings.
This section provides general configuration advice for most scenarios, and specific guides for:
If you stop using the Inbound Gateway, make sure to restore your MX records to their previous state. Failure to do this might impact delivery of incoming email.
To enhance service stability and provide a level of failover, Coro recommends retaining your organization's original MX records in your DNS but configured as lower priority than the Coro Inbound Gateway MX record. By keeping your original DNS records, any interruptions to the availability of the Coro service mean that emails are sent instead to servers defined in lower-priority MX records (the default behavior of SMTP).
MX record priority is determined by the lowest number applied. In other words, an MX record priority value of 10 is treated as higher priority than a value of 20.
Keep a note of your original MX records as these are required for configuration in the Coro console.
Updates to DNS records can take up to 24 hours to take effect.
Coro continuously monitors your DNS settings to ensure that your Inbound Gateway MX records are correctly configured. Any identified issues are reported in the Coro console and emailed to admin users. For more information, see Continuous monitoring.
To configure MX records in Microsoft 365:
Sign into the Exchange Admin console with administrator credentials.
Go to Home > Settings > Domains > [YOUR EMAIL DOMAIN].
Select the DNS records tab.
In the Microsoft Exchange section, locate the MX record entry:
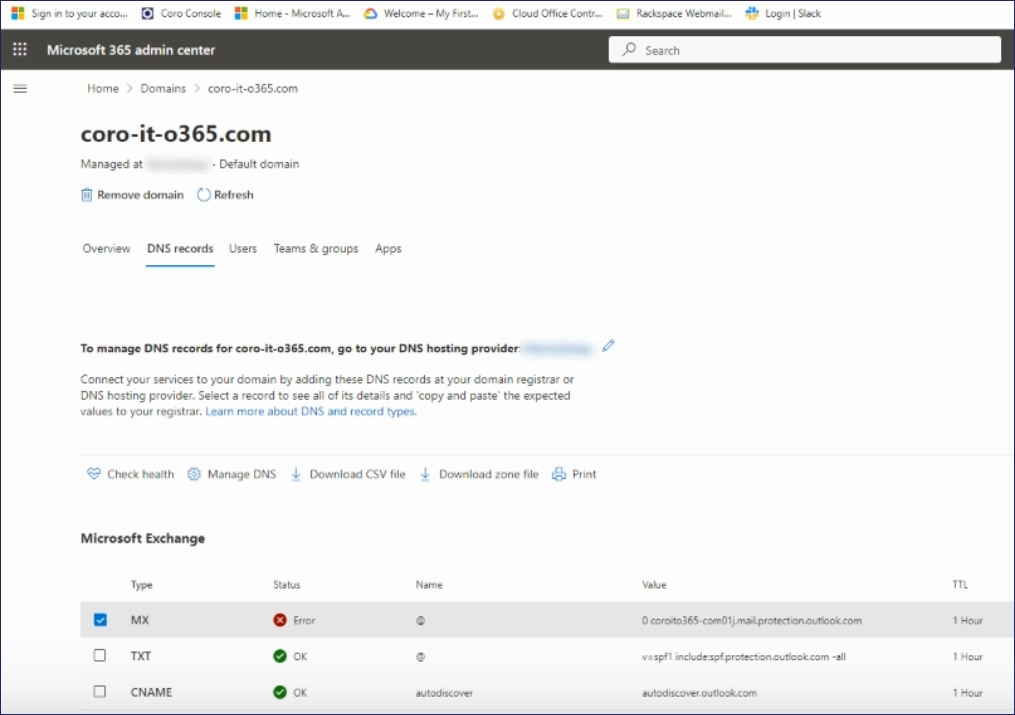
Select the record to view the MX record dialog.
Make a note of the current MX record. For example, “mycompany-mail.protection.outlook.com”. Coro uses this information to define your SMTP relays in your workspace configuration.
Add a new entry for the Coro Inbound Gateway MX record:
Exchange Admin might give validation warnings or errors regarding the new MX record not matching expected values. You can safely ignore this.
Select Done to close the dialog.
To configure MX records in Google Domains Service (for organizations who registered their domains using Google DNS):
Sign into Google Domains Service (https://domains.google.com/) with your administrator credentials.
Select your domain, then select Manage:
Select DNS.
Make a note of the current MX records. Coro uses this information to define your SMTP relays in your workspace configuration.
(Recommended) Back up the current DNS settings as a precaution by selecting Export DNS records.
Set Type as “MX” and add a Data entry corresponding to the Coro Inbound Gateway MX record address.
Add the Coro Inbound Gateway address with the lowest priority number (giving it highest priority in the list). Other servers in the list should be the original Google servers:
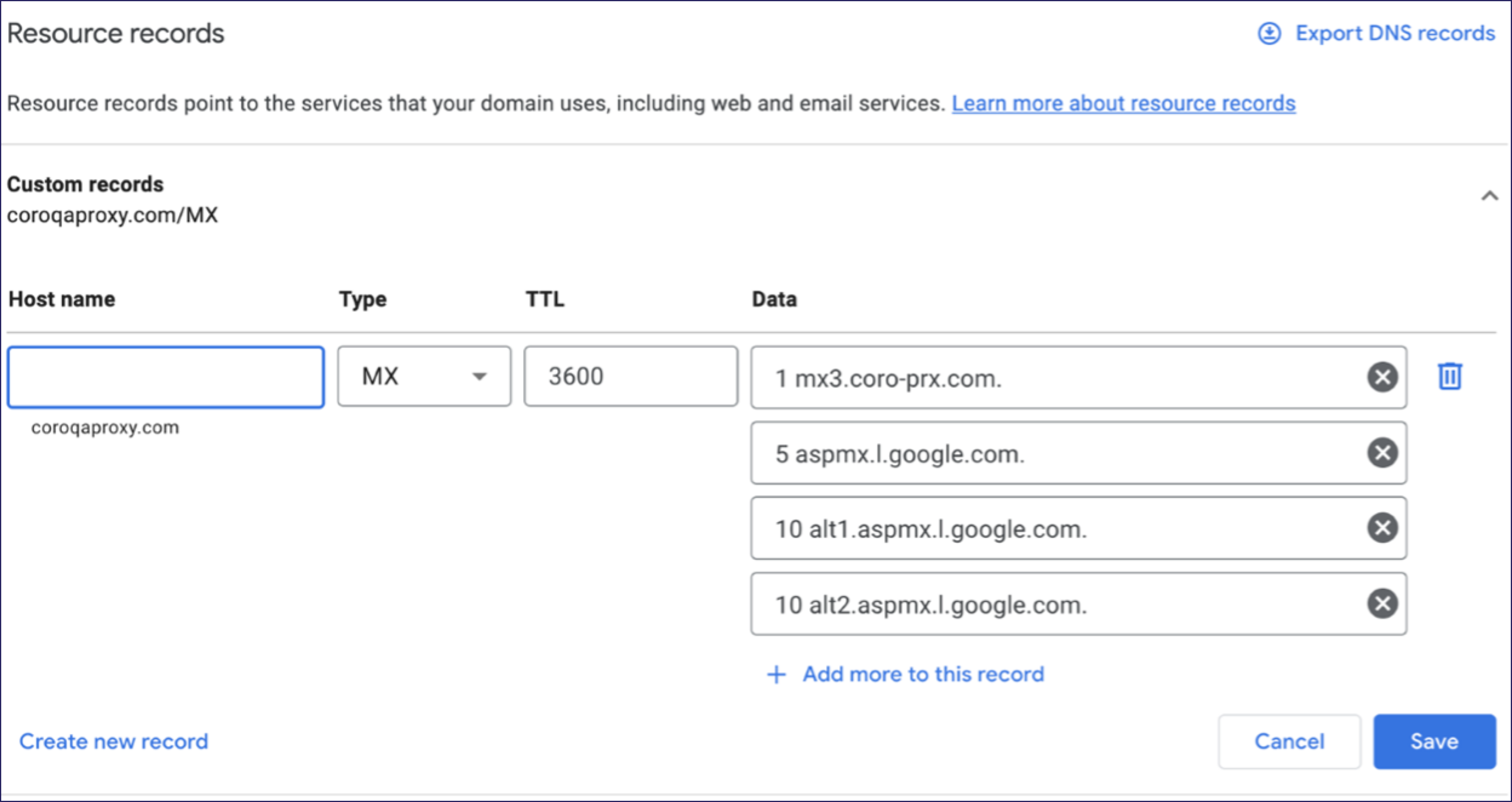
Select Save.
If Google asks for confirmation for overriding the existing configuration, select Yes.
Verify and re-add missing records such as SPF if you find this was overridden by these changes. To do this, select Create new record > SPF, add the required data, then select Save:
Coro continually monitors the operation of the Inbound Gateway in connection with your defined email domains and DNS settings.
If Coro identifies any configuration issues related to your MX records that affect service operation, Coro notifies admin users through the console and via email.
For example, if you change the MX record order in your DNS settings so Coro is no longer the highest priority, emails might not be routed through the Inbound Gateway. This means your incoming emails are not checked or protected by Coro.
View test failure information in the Test status column against your domain: