Using the remote shell to access endpoint devices
Coro includes a remote shell capability that allows admin users with sufficient permissions to access remote endpoint devices in the event that a compromised device must be isolated from the network. Through the shell, you can execute commands on the device to investigate the cause of an issue in a secure and segregated environment.
Managed Service Provider (MSP) admin users with sufficient permissions can access the global devices page to access remote devices across parent (channel) and descendant workspaces.
The remote shell feature runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux devices, and supports a maximum of 10 concurrent connections per device.
If a remote shell session is inactive for 10 minutes, Coro automatically closes the connection.
Prerequisites
To access a shell on a remote device, make sure the following prerequisites are satisfied:
- You have enabled either the Endpoint Security or Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) modules in your Coro workspace.
- The device is online.
- The Coro Agent is installed on the device.
- The device is connected to your Coro workspace.
Activating a remote shell
To activate the remote shell on a device:
From the Actionboard, select the Protected Devices panel:
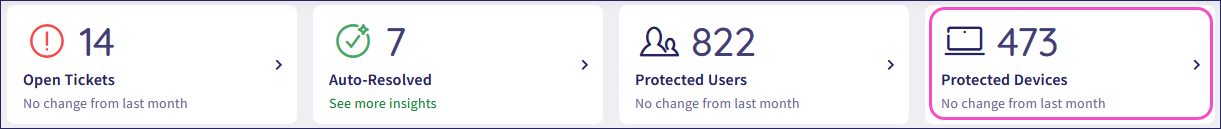
Coro displays the Devices page:
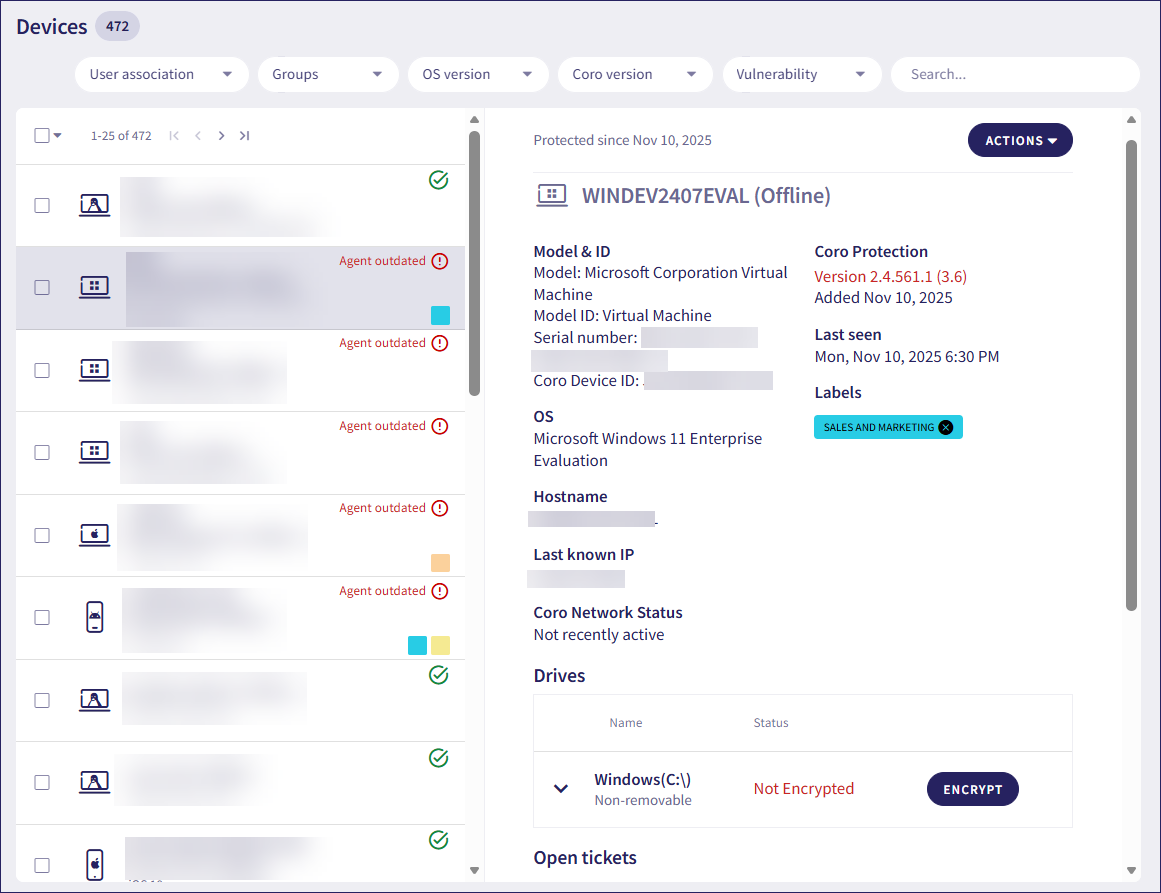
Select a device in the left-hand pane, then select ACTIONS from the right.
Select Open remote shell from the list of actions:

If Open remote shell does not appear in the actions list, check you have met the prerequisites.
After the connection has succeeded, the remote shell dialog appears showing the list of available commands:
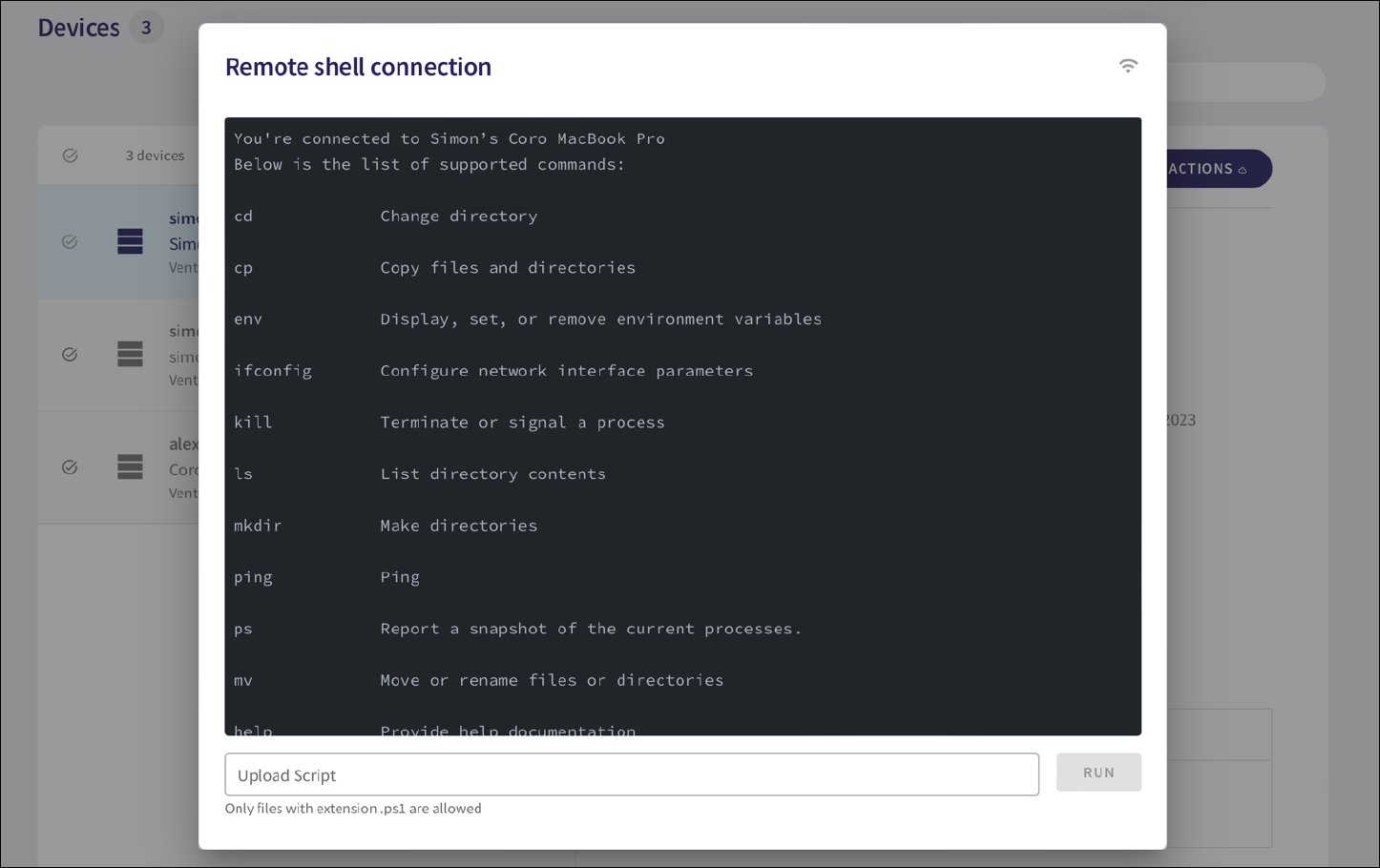
Enter your commands at the shell command prompt.
For Windows devices, you can additionally upload and execute PowerShell scripts on the remote device. Enter the local location of your script file into the Upload Script box and select RUN to remotely execute the script.
This function supports script files with a .ps1 extension.
Remote shell commands
The Coro remote shell provides a command line prompt on the remote device with a limited command set. The following table summarizes the available commands, platform availability, and a basic usage syntax.
To learn more about each command, including extended syntax options and examples, refer to the command reference documentation provided by Microsoft (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/) or Apple (https://support.apple.com/en-gb/guide/terminal/welcome/mac).
| Command | Basic syntax | Description | Windows | macOS | Linux |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd | cd [<directory>] | Change to the current user home directory, or to the specified working directory | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Copy-Item | Copy-Item <file> <target directory> | Copies an item from one location to another | Yes | No | No |
| cp | cp <file> <target directory> | Copies an item from one location to another | No | Yes | Yes |
| env | env | Display all current environment variables and their values | No | Yes | Yes |
| Get-FileHash | Get-FileHash <file> [[-Algorithm] <algorithm>] | Compute the hash value for a file using a specified hash algorithm (default: SHA256) | Yes | No | No |
| Get-LocalUser | Get-LocalUser | Display local user accounts | Yes | No | No |
| Get-Service | Get-Service [<service name>] | Display the run status of the named service (or all services) | Yes | No | No |
| help | help | Display this list of commands | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ifconfig | ifconfig | Display all current TCP/IP network configuration values | No | Yes | Yes |
| ipconfig | ipconfig | Display all current TCP/IP network configuration values | Yes | No | No |
| kill | kill <Process ID> | Kill a process | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ls | ls [<directory>] | Display the contents of the current or specified directory | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| mkdir | mkdir <New directory name> | Create a new directory | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| mv | mv <file/directory> <target directory> | Move a file or directory | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| netstat | netstat | Display protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections | Yes | No | No |
| ping | ping <target IP address> | Send a network ping to a specified IP address | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ps | ps | Display information about system processes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| pwd | pwd | Display the current directory | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| shutdown | shutdown | Shutdown the target device | Yes | No | No |
| start | start <path to process executable> | Start a process | Yes | No | No |
| start-service | start-service <service name> | Start a service | Yes | No | No |
Troubleshooting
The remote shell takes a long time to respond to commands.
If you experience a delay in response to your entered commands (longer than 10-20 seconds), refresh the Coro console webpage and restart the remote shell connection.
The "Open remote shell" action is not present for a device on the Devices page.
A prerequisite condition for the remote shell function has not been met. Review the prerequisites.
The "Open remote shell" action is greyed out and not available to select.
The version of the Coro Agent running on the remote device is earlier than the minimum required version for this feature. Update the Agent version to enable the remote shell functionality.
An executed PowerShell script stops unexpectedly.
Make sure your script uses only valid PowerShell commands and does not include any commands that require user intervention.