Introducing Security gaps
Coro's Security gaps help you identify and resolve workspace misconfigurations that are not aligned with Coro's best practices and might reduce protection. You can monitor these gaps and take corrective action to maintain a unified security posture across your Coro workspace. Security gaps are grouped by type, and most include corrective steps you can apply with a single action.
Managed Service Provider (MSP) admin users with sufficient permissions can also access global security gaps to view and manage gaps across parent and descendant workspaces.
Use Security gaps to:
Continuously monitor for workspace misconfigurations.
Detect misconfigurations across your Coro workspace.
Fix misconfigurations using automated or manual actions.
Security gaps highlight areas where workspace configurations are incomplete or not aligned with Coro's best practices. They are not threat detections.
Coro surfaces opportunities to improve security by detecting areas where configurations might be incomplete or protections not fully applied, including but not limited to:
Endpoint security settings on user devices.
Scheduled scans for sensitive data.
Assigning protected users.
Enabling email threat scanning.
To access Security gaps:
From the sidebar, select Security Gaps:

Alternatively, from the Actionboard, select View all at the top of the Security Gaps dashboard panel:
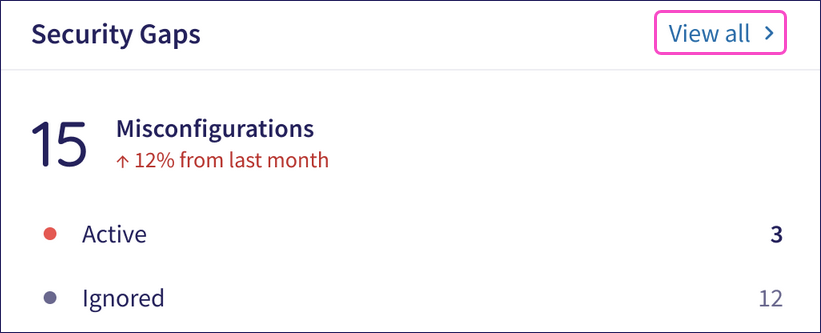
Coro displays the Security gaps page:
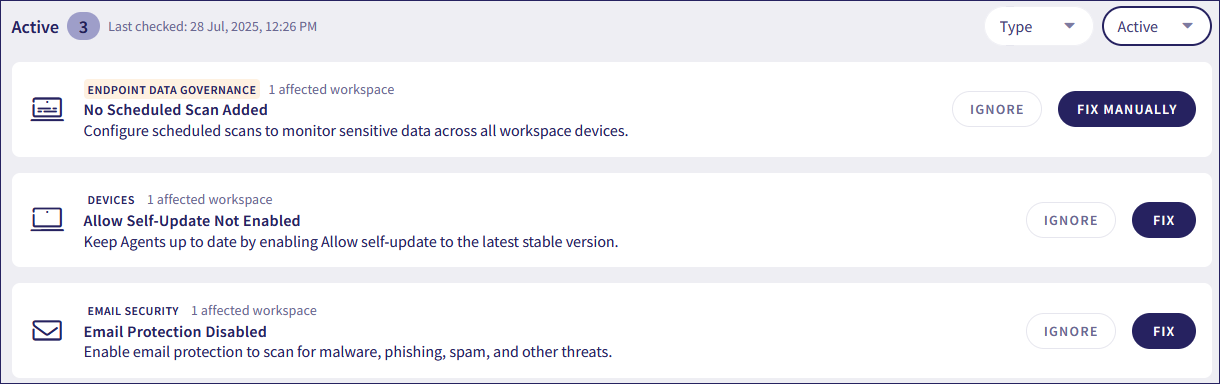
On this page, you can:
Review active and ignored gaps for your workspace.
Take corrective action.
Filter gaps by type and state.
Coro displays the following details for each listed gap:
Gap type.
Number of workspaces affected by the gap.
Gap name and description.
For more information, see Managing security gaps.