Risk types
Organizations face many risks to their data and some risks can develop unintentionally (for example, sharing files or sending information to the wrong recipient). However, the most common threats emerge from data misuse and malicious activities.
The major risk areas for organizations include:
Data theft or loss
Data theft, loss, breach, or damage can cause financial and reputational loss to an organization.
Business continuity
The cost of recovery from a severe data breach can be too high.
Regulatory compliance
Almost all organizations are now bound to comply with one or more regulations surrounding customer, user, and employee data and privacy.
Insurance requirements
The need for organizations of all sizes to comply with ever-increasing insurance policy requirements.
Business data in this context refers to data files, emails, or communications used and processed as a part of an organization's operations. This data may be stored on user endpoint devices, internal server systems, or externally in other cloud applications.
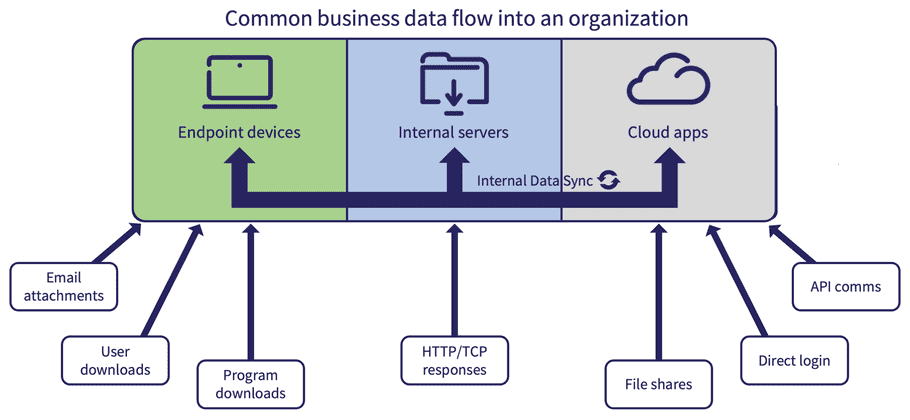
Endpoint devices transfer data through email attachments, user-initiated downloads, and program-executed downloads. Organizational internal servers may connect to external services and use protocols like HTTP or TCP for requests.
Cloud applications (while often external to an organization) facilitate the transmission of data through file sharing, API connectivity, and direct login access for user accounts within the company.
Sensitive business data can be transmitted in several ways:
- Created internally and transmitted/shared to legitimate services outside of the organization.
- Imported from external sources. For example, email attachments or downloads.
- Auto-synced between employee devices and external services. For example, cloud drives.
- Auto-synced, moved, or copied between services/devices inside an organization.
note
Data can be manipulated by automated processes within computer systems (as part of services and applications), in addition to user-managed sources such as email or databases. Users may be unaware of the automated activity between services and APIs.
Every entry point carries a potential risk for malicious activity. Automated synchronization between applications can also facilitate the spread of malicious activity within an organization. Organizations often balance these risks while securing data to support legitimate business operations.
Coro offers a comprehensive solution for managing protection and monitoring across cloud apps, users, devices, email, and data governance.